序言
去年花里逢君别,今年花开又一年。
对JavaWeb中Context的学习,设计模式yyds。
名词解释
文中出现的所有名词解释:
Web容器:Tomcat,JBoss
Tomcat架构
Tomcat大家都比较熟悉了,Connector连接器负责外部交流,Container容器负责内部处理。
Container组件,容器,内部实现了4种子容器:
4种子容器: Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper ,这四种容器是父子关系。
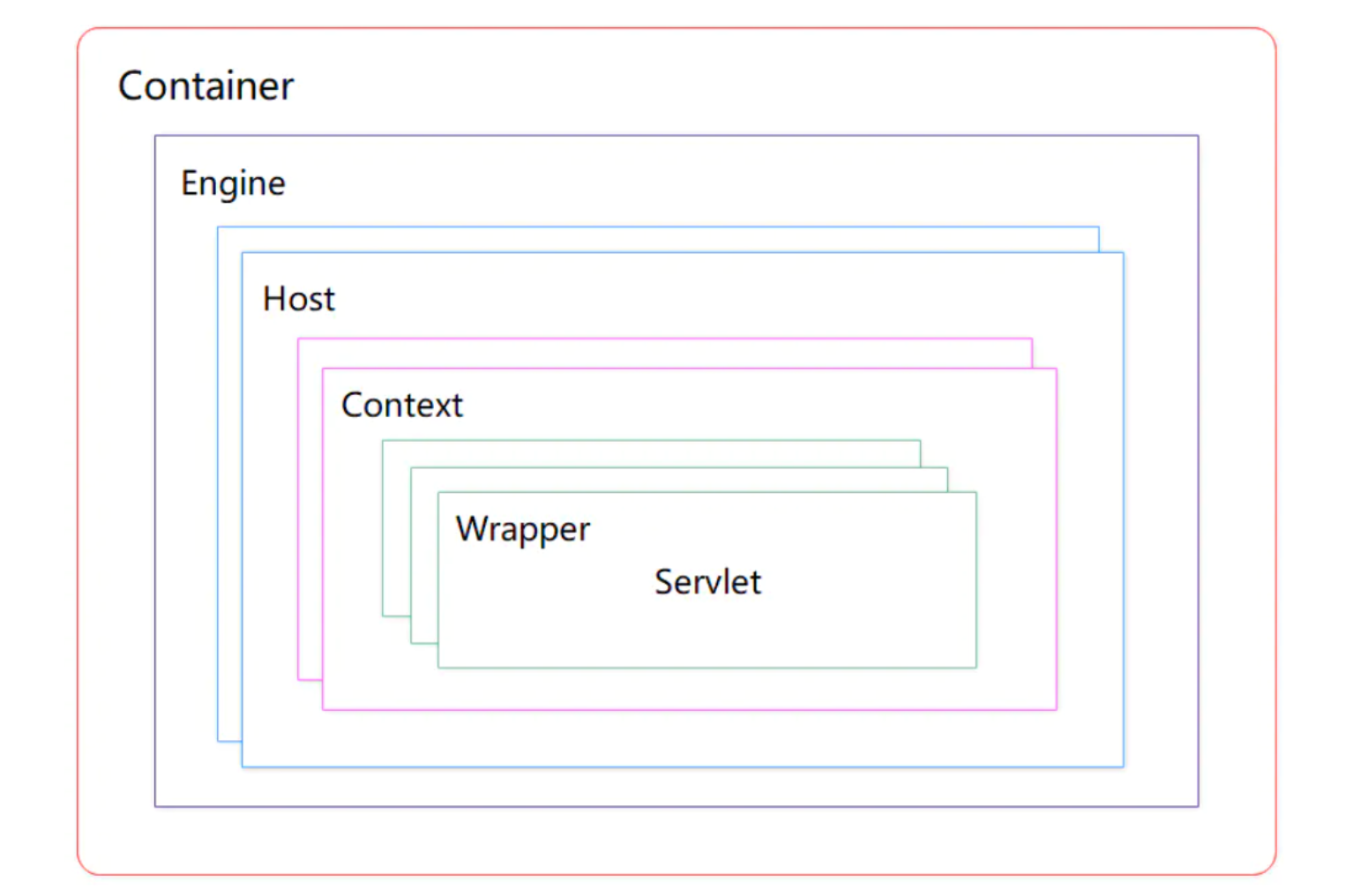
- Engine: 最顶层容器组件,可以包含多个Host。实现类为
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine - Host: 代表一个虚拟主机,每个虚拟主机和某个域名Domain Name相匹配,可以包含多个Context。实现类为
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost - Context: 一个Context对应于一个Web 应用,可以包含多个Wrapper。实现类为
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext - Wrapper: 一个Wrapper对应一个Servlet。负责管理 Servlet ,包括Servlet的装载、初始化、执行以及资源回收。实现类为
org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper
Context在Tomcat中代表一个Web应用的抽象表示,下文重点看Context部分。
三种Context
ServletContext
StandardContext
ApplicationContext
ServletContext
ServletContext是javax.servlet包下的接口(规范),它不属于Tomcat也不属于Spring家族。
它的本意是可以对某个Web应用的各种资源和功能进行访问。
Web容器在启动时,它会为每个Web应用程序都创建一个对应的ServletContext对象。它代表当前Web应用,并且它被所有客户端共享。
StandardContext
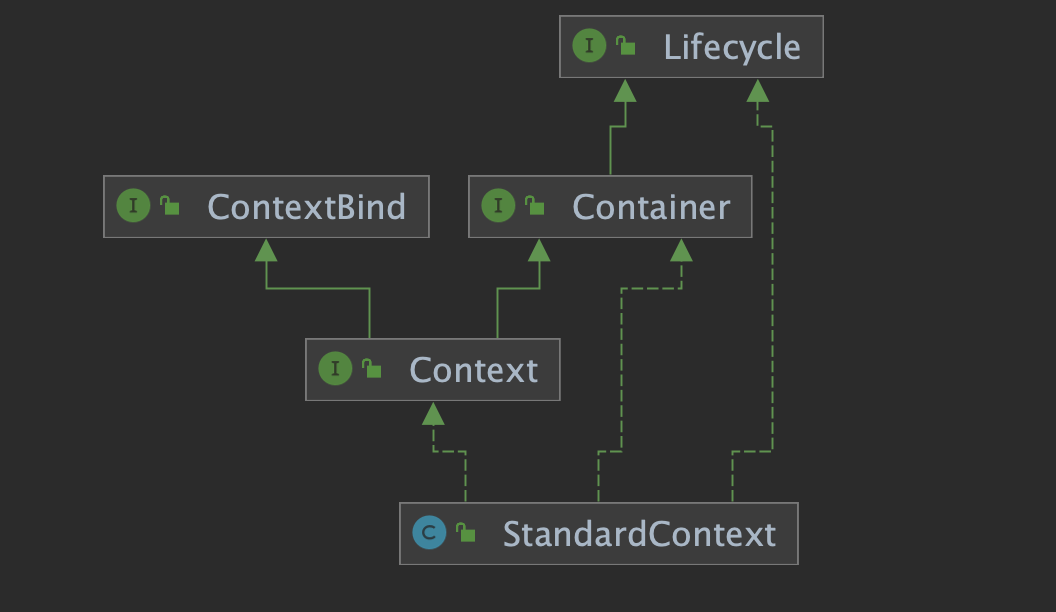
Tomcat架构图中的Context其实就是个接口,Tomcat内部对Context接口的默认实现为StandardContext类。
StandardContext是一个Web应用在Tomcat内部的具体对象。
ApplicationContext
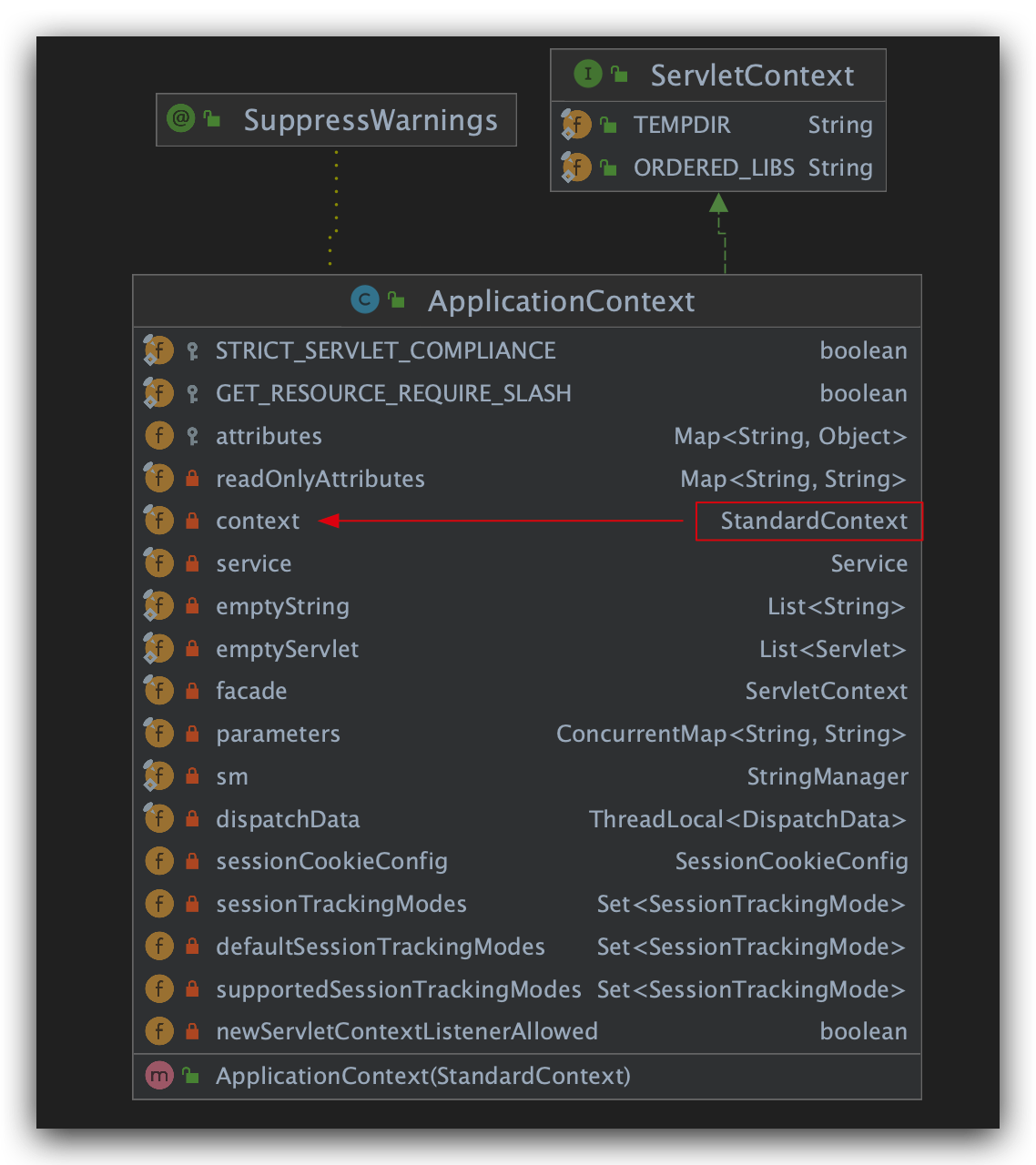
ApplicationContext其实更像是为了满足ServletContext规范而对StandardContext的一种封装。
在Tomcat内部,ApplicationContext是ServletContext接口的具体实现。
而Tomcat惯用Facade方式,因此我们一般获取的ServletContext实例是ApplicationContextFacade对象
ApplicationContextFacade对象其实就是对ApplicationContext做了一层包装。
搞搞StandardContext
web.xml信息装配到StandardContext中
如果你debug过tomcat的源码,你会发现,其实在tomcat启动的时候,会执行valve责任链那一套,来到
Tomcat 层级调用组件的start()方法,执行StandardContext.startInternal() 方法:
1 | //挑重点说 |
可以看出来,在startInternal()方法中调用fireLifecycleEvent()发布一个”configure_start” 事件。
fireLifecycleEvent方法内部将信号configure_start被包装为一个LifecycleEvent对象event,通知所有的lifecycleListeners。
LifecycleListener是一个接口,接口中的lifecycleEvent抽象方法被ContextConfig实现类进行了重写。
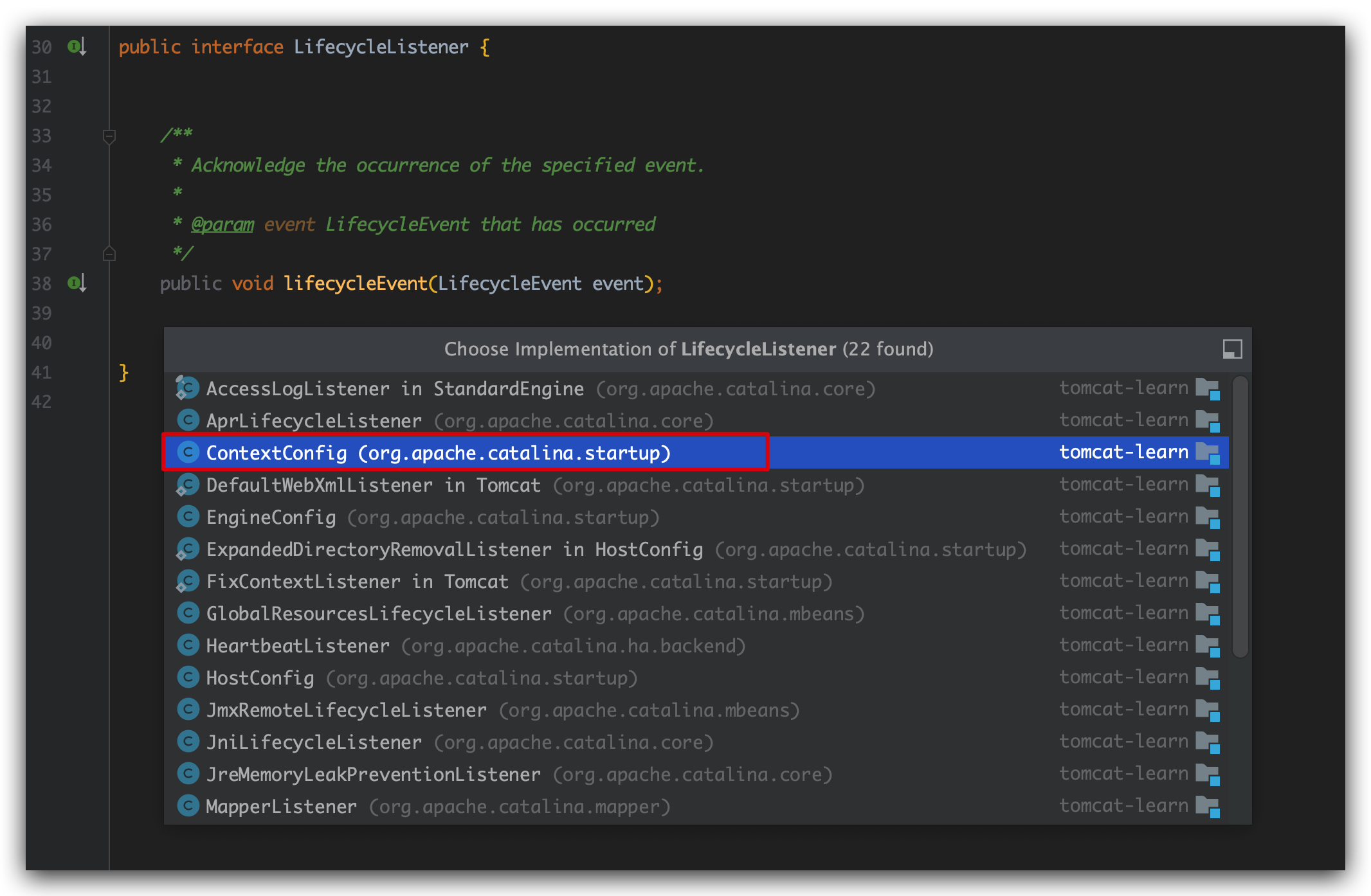
下面是ContextConfig类重写的lifecycleEvent方法,可以看到我们现在满足信号条件会执行configureStart方法。
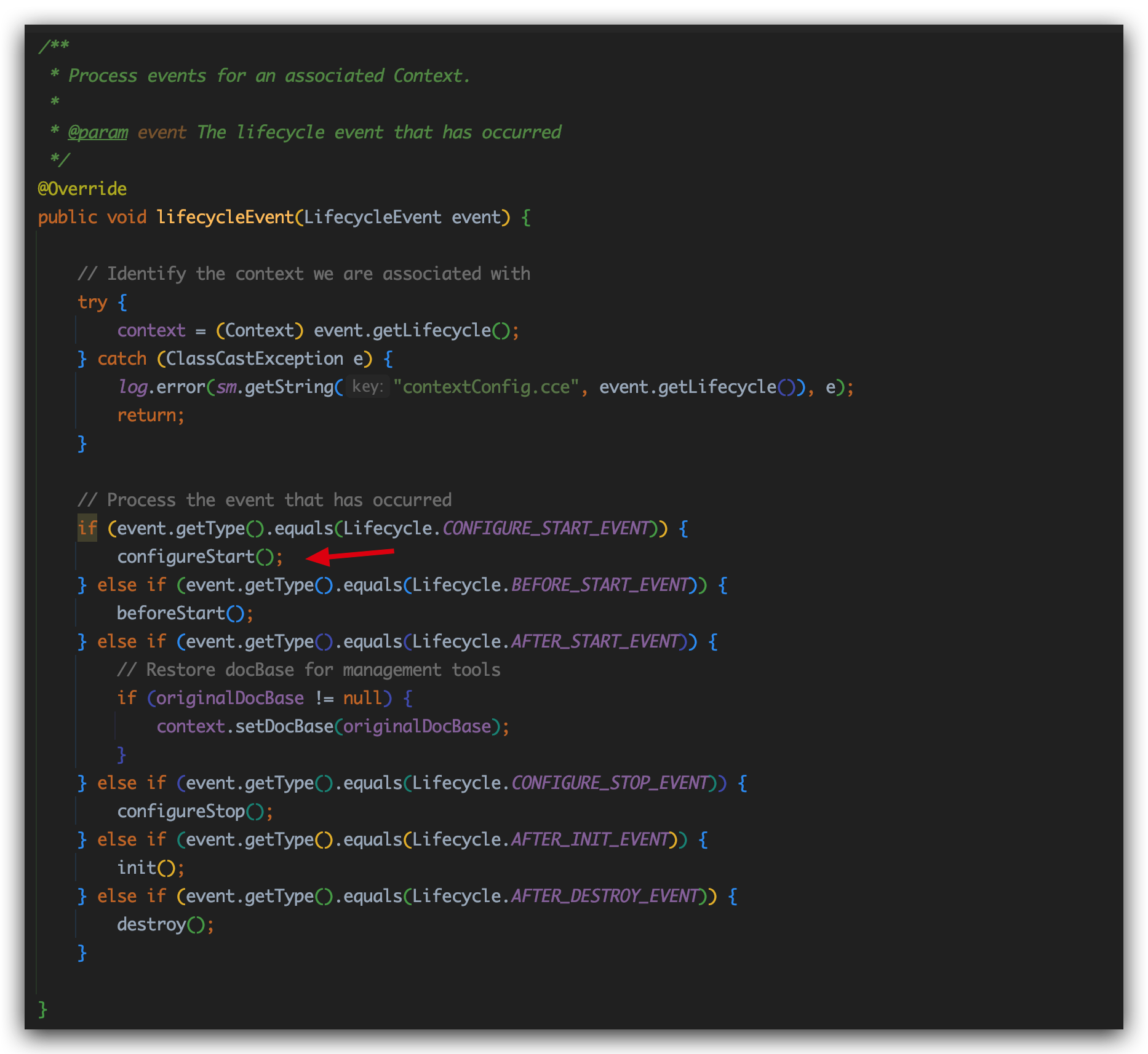
1 | protected synchronized void configureStart() { |
动态调试源码看一眼,确实是StandardContext对象
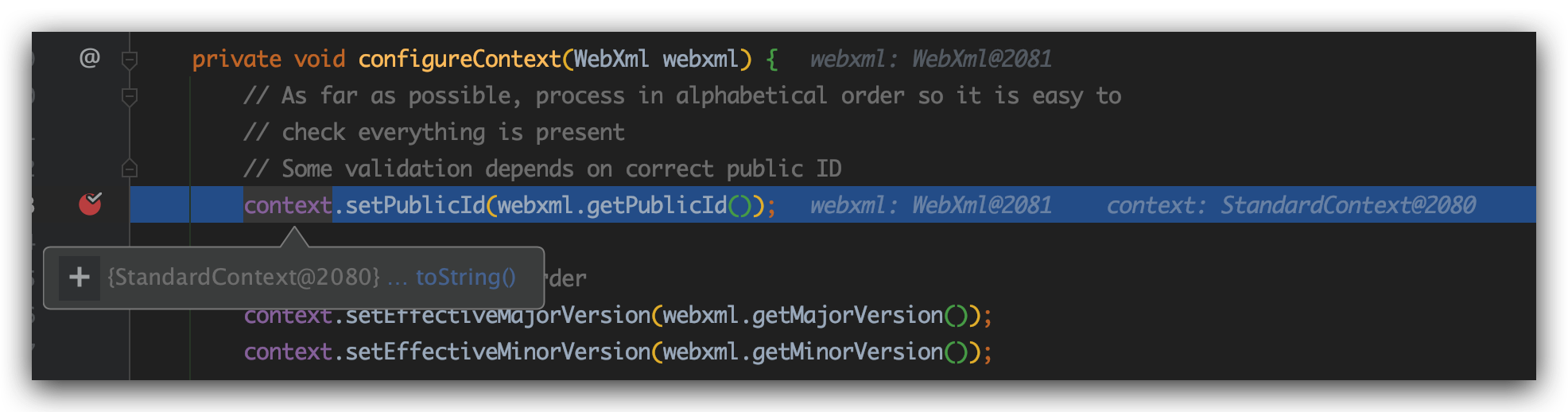
configureContext方法内部其实就是为我们配置filter、listener、filter、filterMap等信息。
1 | private void configureContext(WebXml webxml) { |
执行
configure_start信号目的就是让tomcat将web.xml信息加入到StandardContext中,现在已经结束了。
回到StandardContext.startInternal()方法中:
整合SpringMVC
1 | <web-app> |
我们发现,在springMVC的web.xml通常有这么一节配置:
1 | <!--监听器--> |
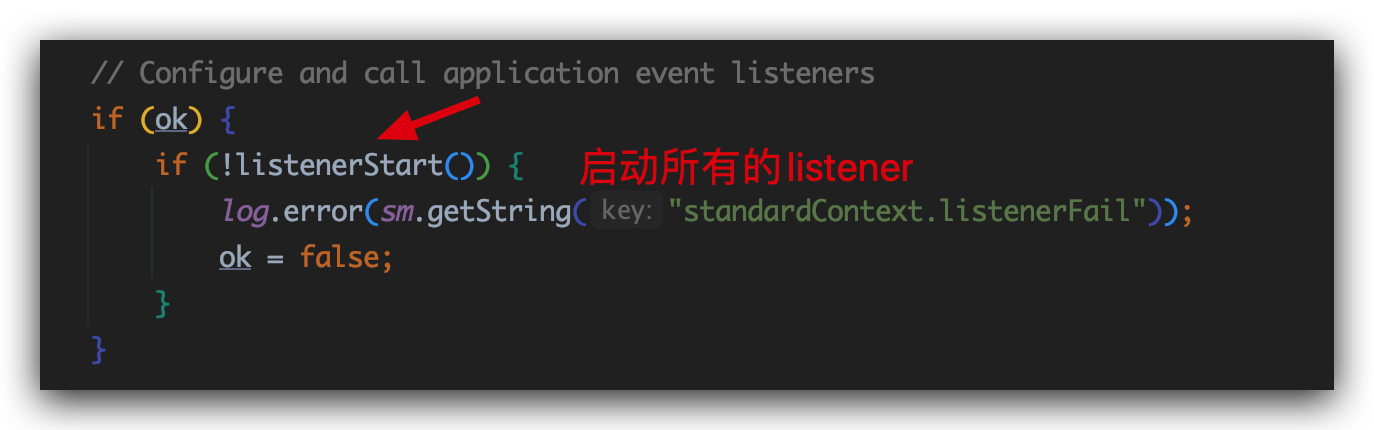
接着上一小节说,如果我们现在将SpringMVC工程打成war包,工程的web.xml就会被解析,这段listener就会被解析进来
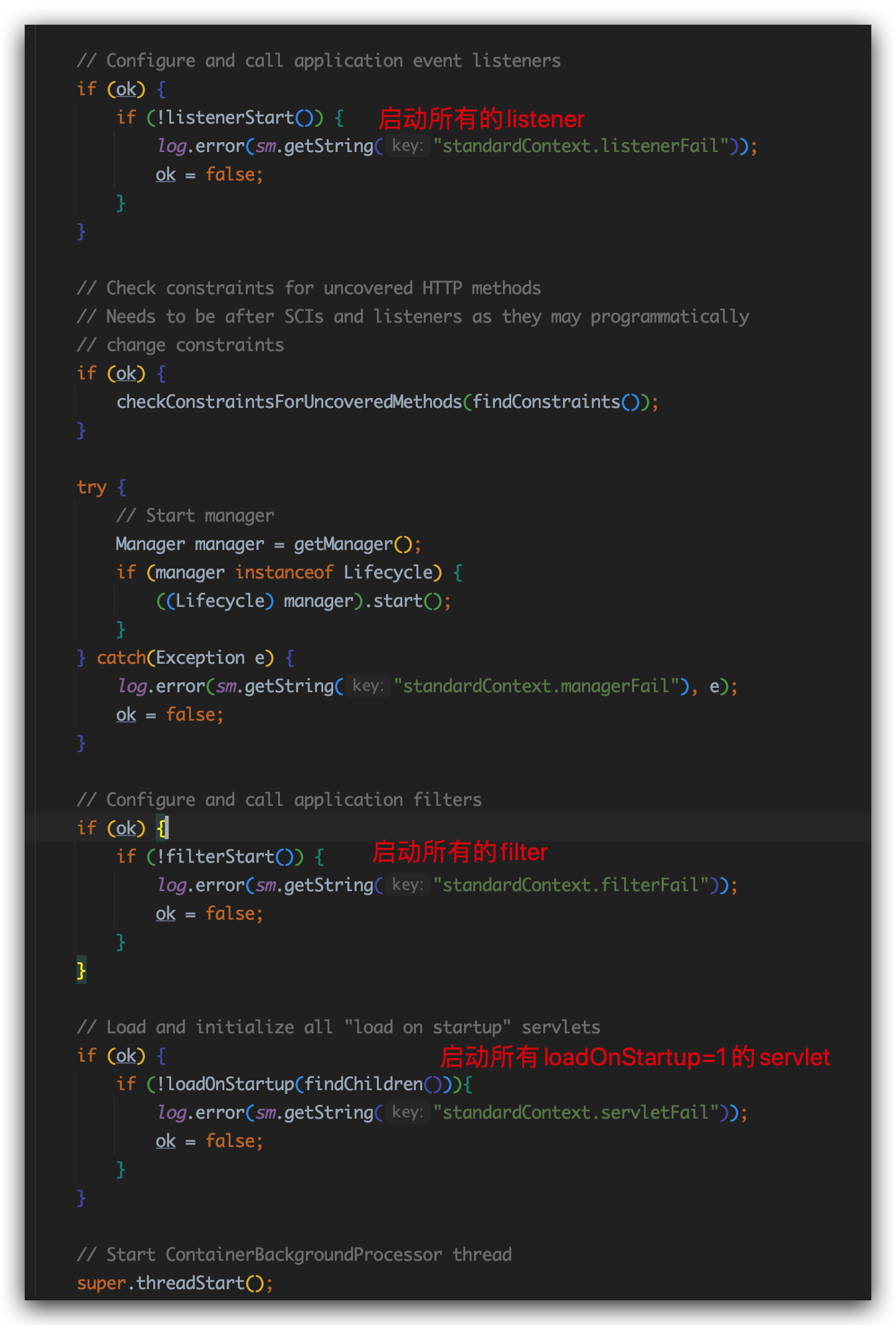
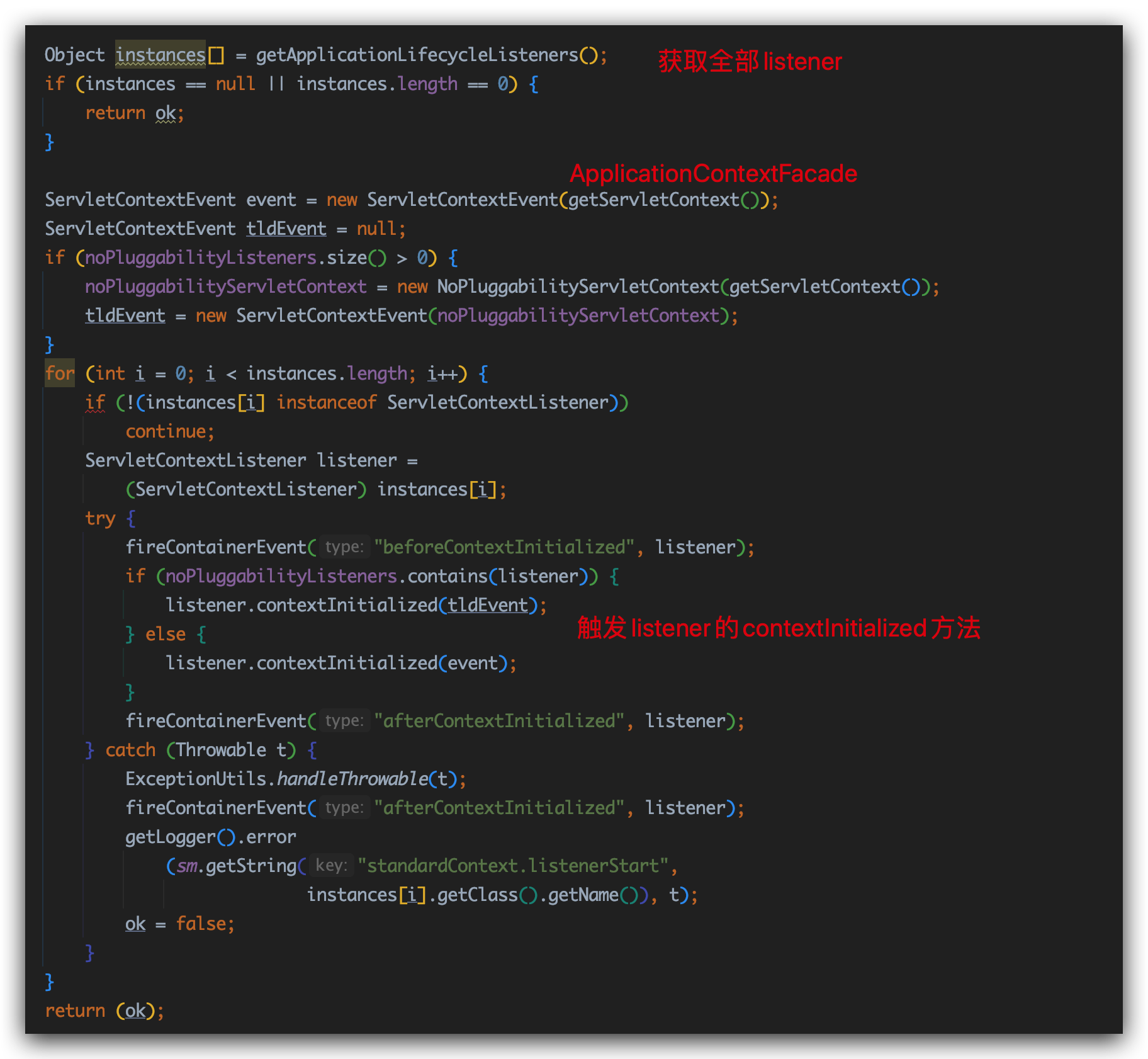
我们进入listenerStart方法,顾名思义就是触发每个listener的方法:
重点片段:
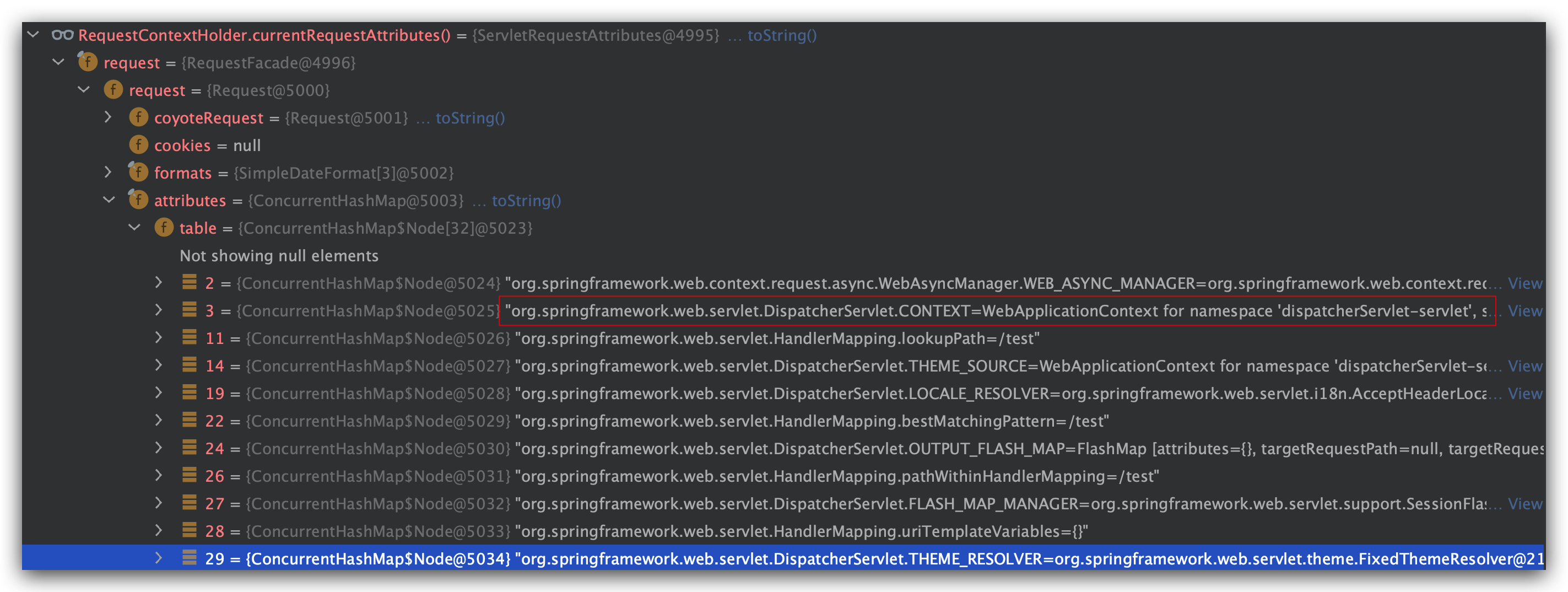
debug看一下,确实触发ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized方法,event包装的是ApplicationContextFacade
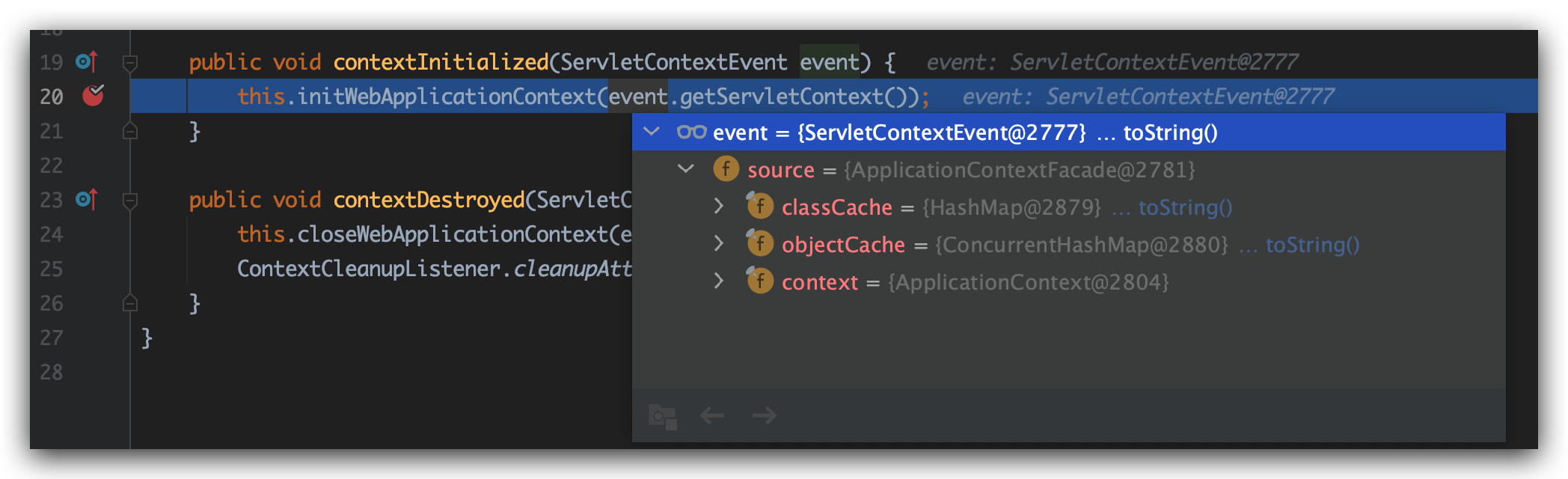

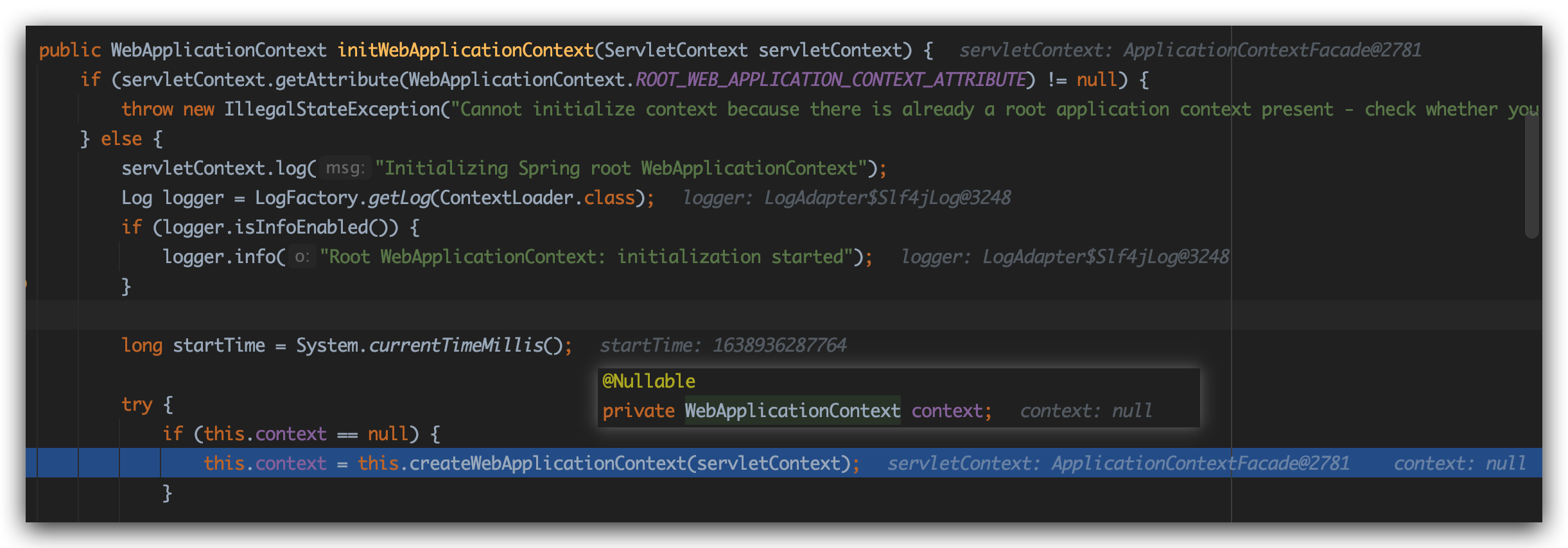
我们直接进入initWebApplicationContext方法
上来就是域对象属性判断:
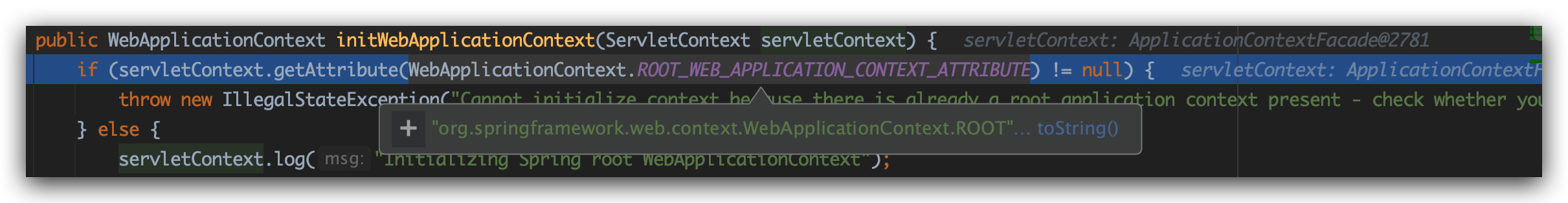
我们传进来的ApplicationContextFacade当然没有这个属性了
来到this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
很明显,这是创建SpringMVC自己的WebApplicationContext
搞搞ApplicationContext
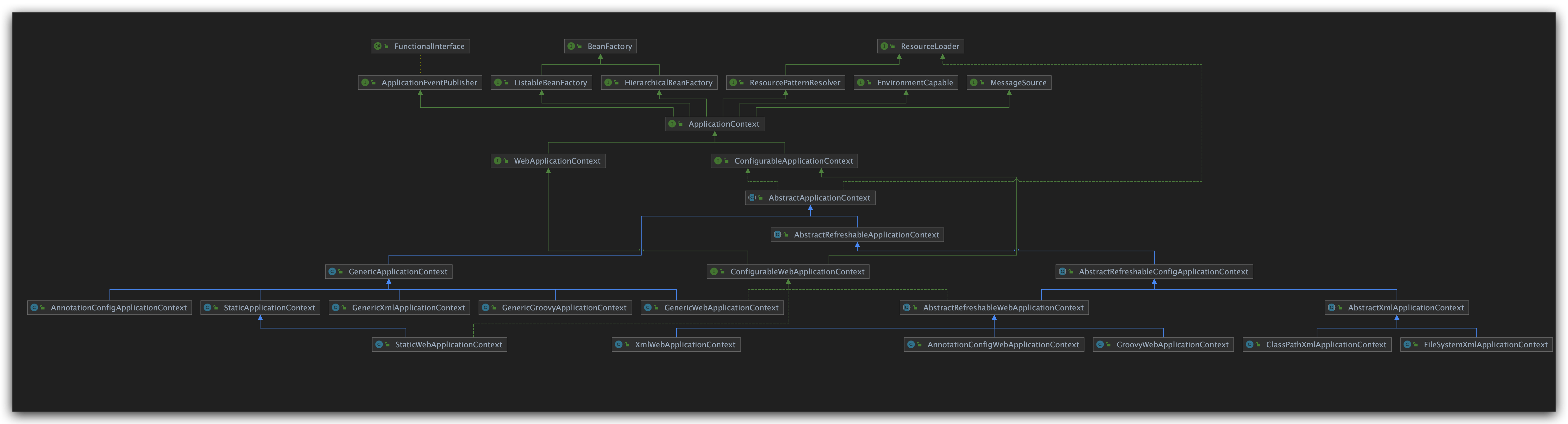
Spring有两个核心接口:BeanFactory和ApplicationContext。都可以代表Spring容器。
什么是Spring容器?Spring容器是生成Bean实例的工厂,并且管理容器中的Bean的生命周期。
应用中的所有组件,都处于Spring的管理下,都被Spring以Bean的方式管理,Spring负责创建Bean实例,并管理他们的生命周期。
和 BeanFactory 类似,它可以加载配置文件中定义的 bean,将所有的 bean 集中在一起,当有请求的时候分配 bean。
另外,它增加了企业所需要的功能,比如,从属性文件从解析文本信息和将事件传递给所指定的listeners。
BeanFactory的实现是按需创建,即第一次获取Bean时才创建这个Bean,而ApplicationContext会一次性创建所有的Bean。
最常被使用的 ApplicationContext 接口实现:
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:该容器从 XML 文件中加载已被定义的 bean。需要提供XML 文件的完整路径。
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:该容器从 XML 文件中加载已被定义的 bean。不需要提供 XML 文件的完整路径。
- WebXmlApplicationContext:该容器会在一个 web 应用程序的范围内加载在 XML 文件中已被定义的 bean。
转换
我们回到”创建SpringMVC自己的WebApplicationContext”这里:

跟进去createWebApplicationContext方法中:
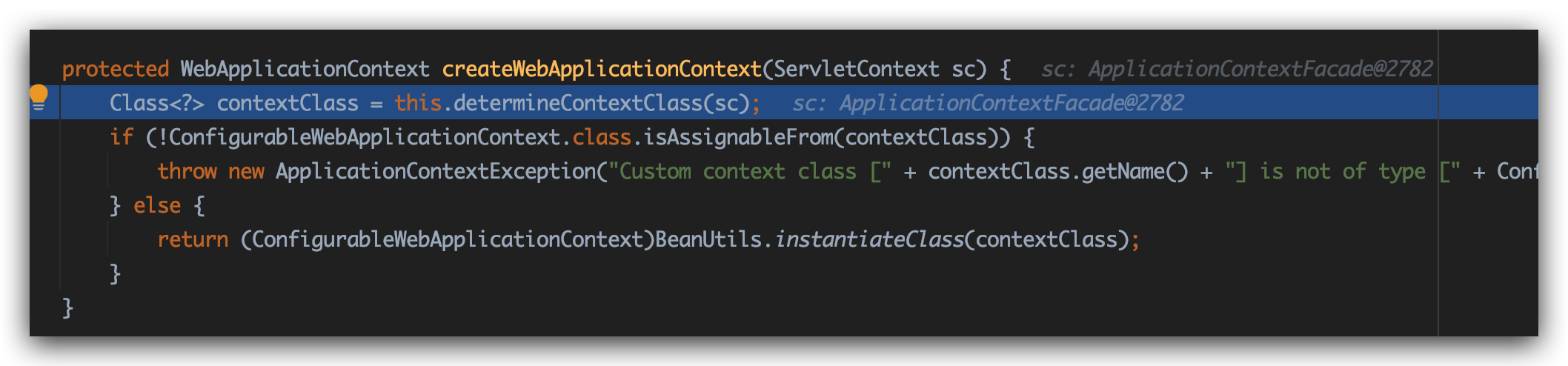
determineContextClass方法:
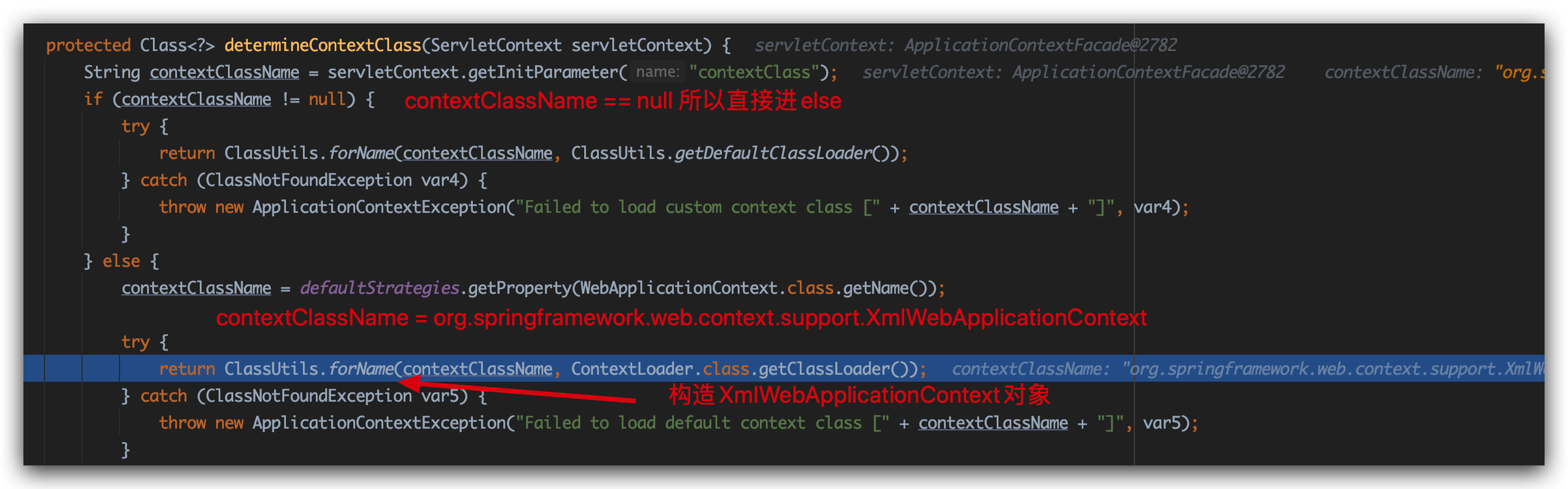
这里的ApplicationContextFacade没有contextClass属性(自己在web.xml可以配置)
那么ClassUtils.forName就为应用返回一个默认的XmlWebApplicationContext类型的Class对象。
返回上级createWebApplicationContext方法,返回值contextClass其实就是XmlWebApplicationContext类对象。
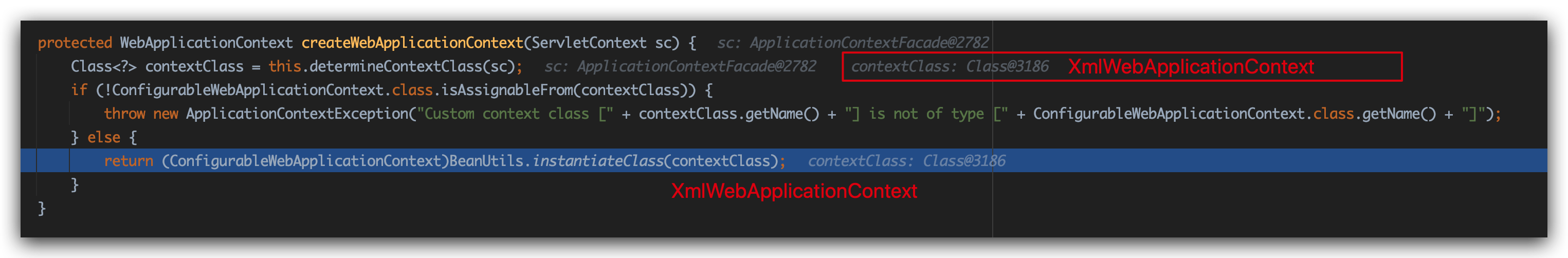
进入BeanUtils.instantiateClass方法,将Class对象进行了实例化,返回了XmlWebApplicationContext的实例化对象,赋值给了ContextLoader类(ContextLoaderListener的父类)的context属性。
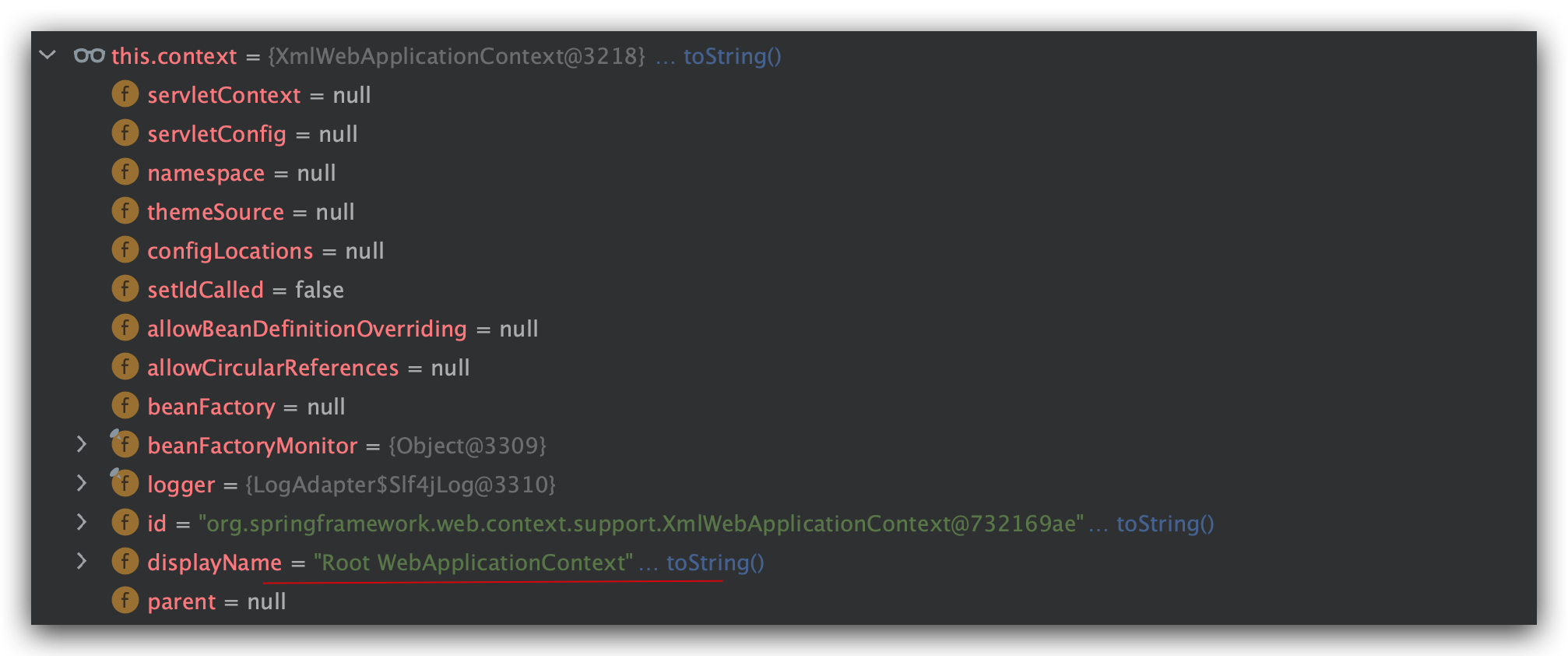
XmlWebApplicationContext是WebApplicationContext的某一个实现类
我们可以看到,其实这里的context已经被标识为”Root WebApplicationContext”了
一路跟下来,我们知道context其实是tomcat内部的ApplicationContextFacade对象被Spring包装为自己的XmlWebApplicationContext对象了。
并且作为“Root WebApplicationContext”,是唯一的。
ok继续向下看,parent为null,进入configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法:
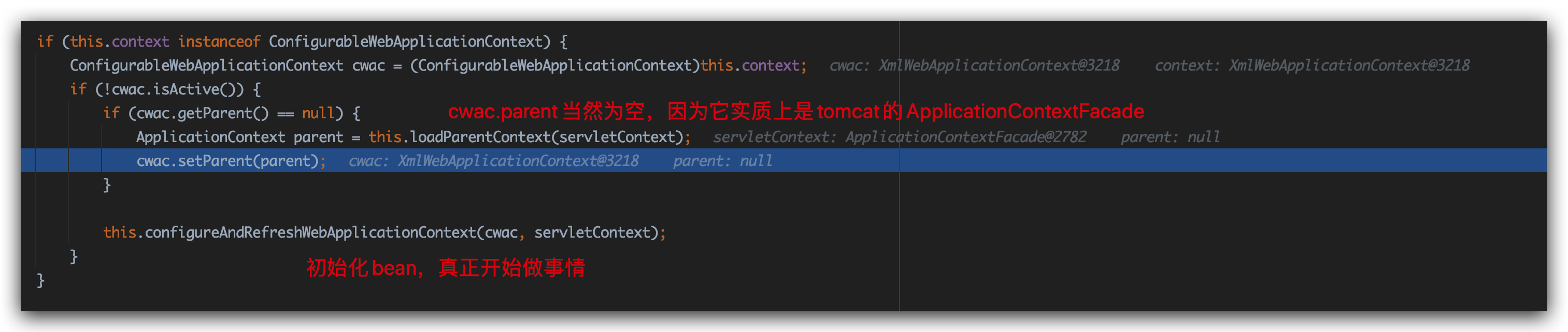
之后挑重点说:
1 | configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext() |
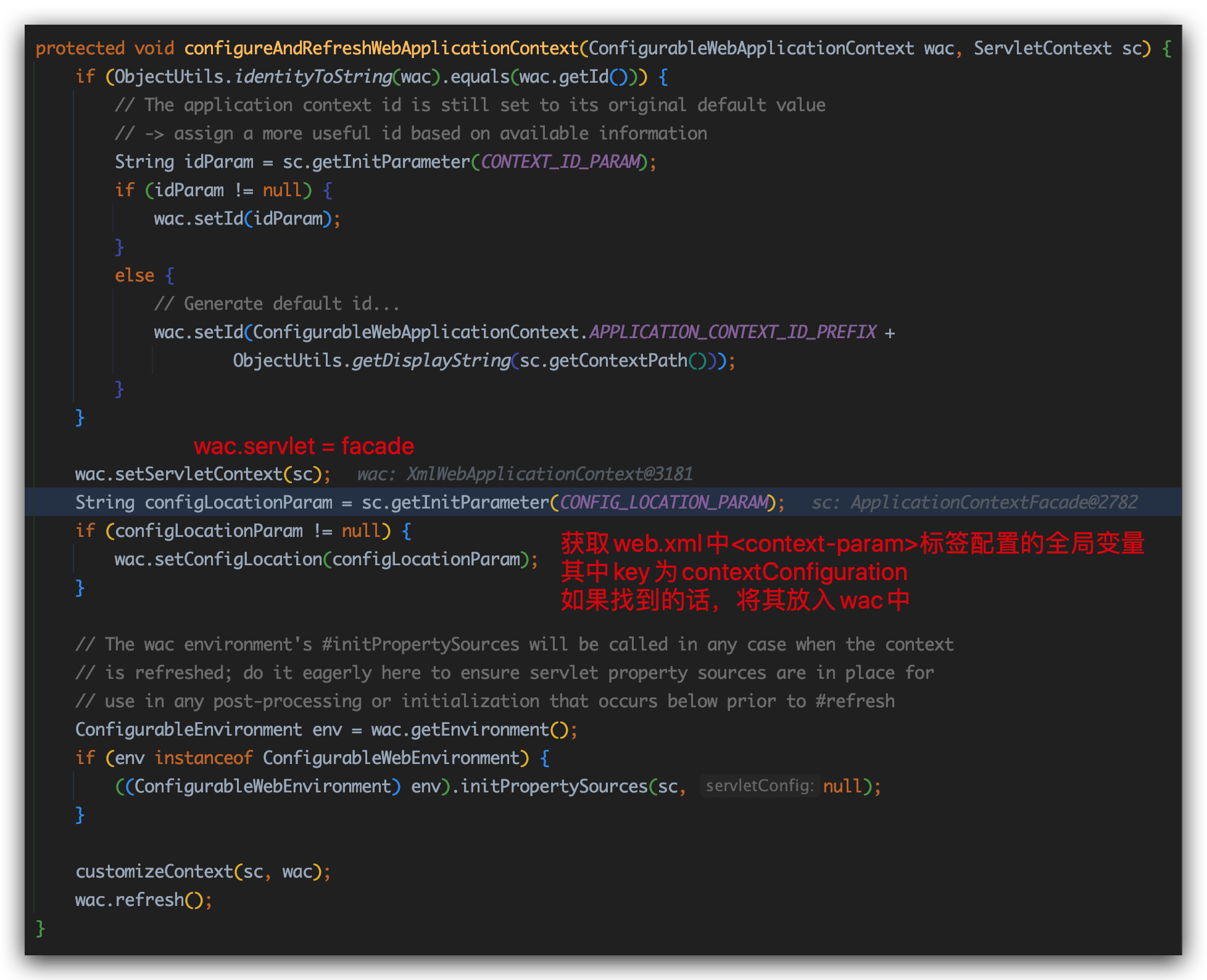
contextConfigLocation是要告诉ContextLoaderListener要把哪些Bean注入到XmlWebApplicationContext管理的BeanFactory。
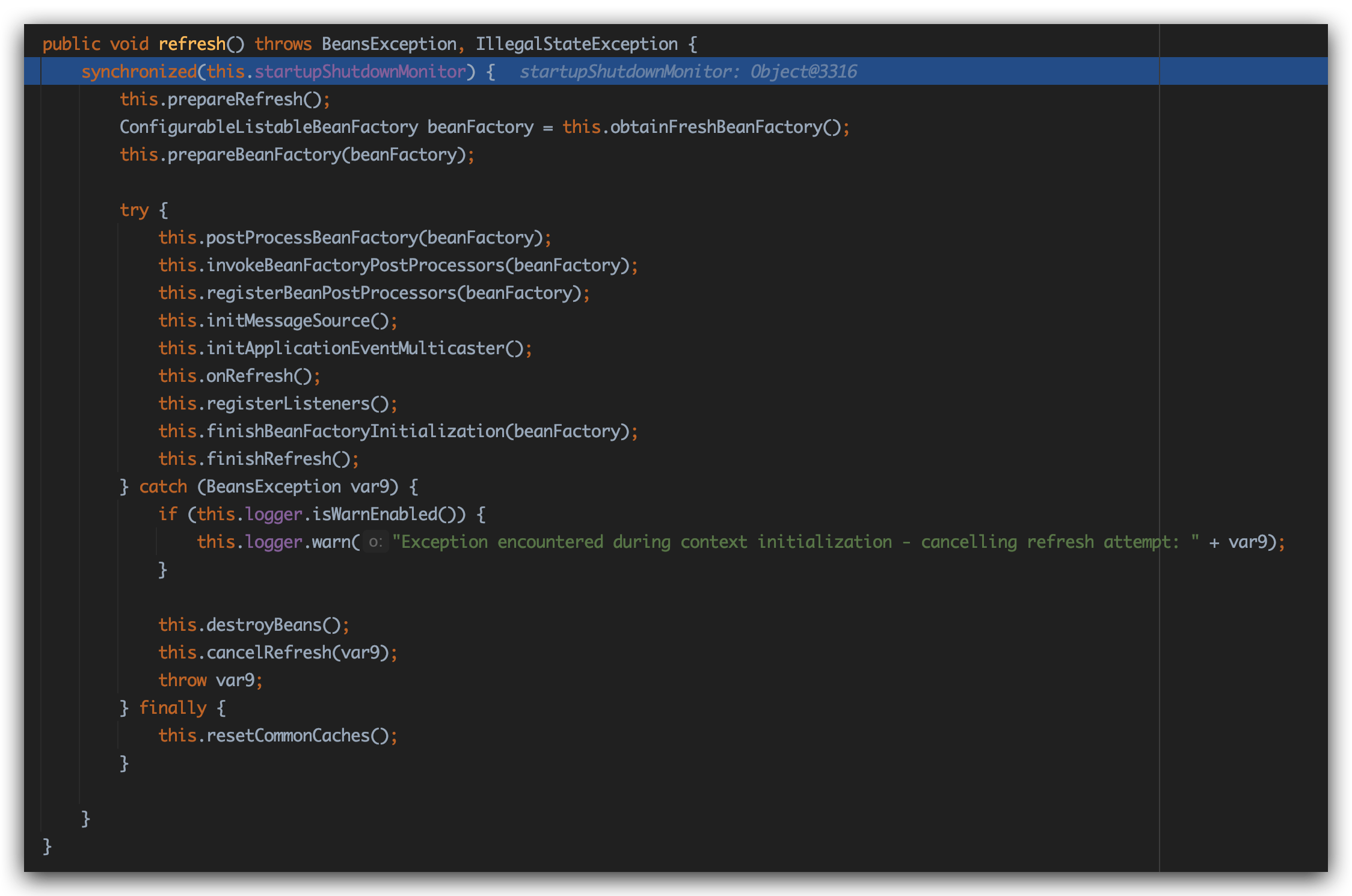
refresh才开始真正初始化组件。
总结:
我们在SpringMVC工程中配置好的web.xml中的listener类型ContextLoaderListener,会监听Web容器(tomcat)的初始化事件。ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized方法中,Spring会将tomcat中唯一的ApplicationContextFacade对象包装为XMLWebApplicationContext对象并标识为全局唯一的Spring根容器”ROOT WebApplicationContext”。
融合
当我们完成bean初始化之后,还是要回到最开始的initWebApplicationContext方法
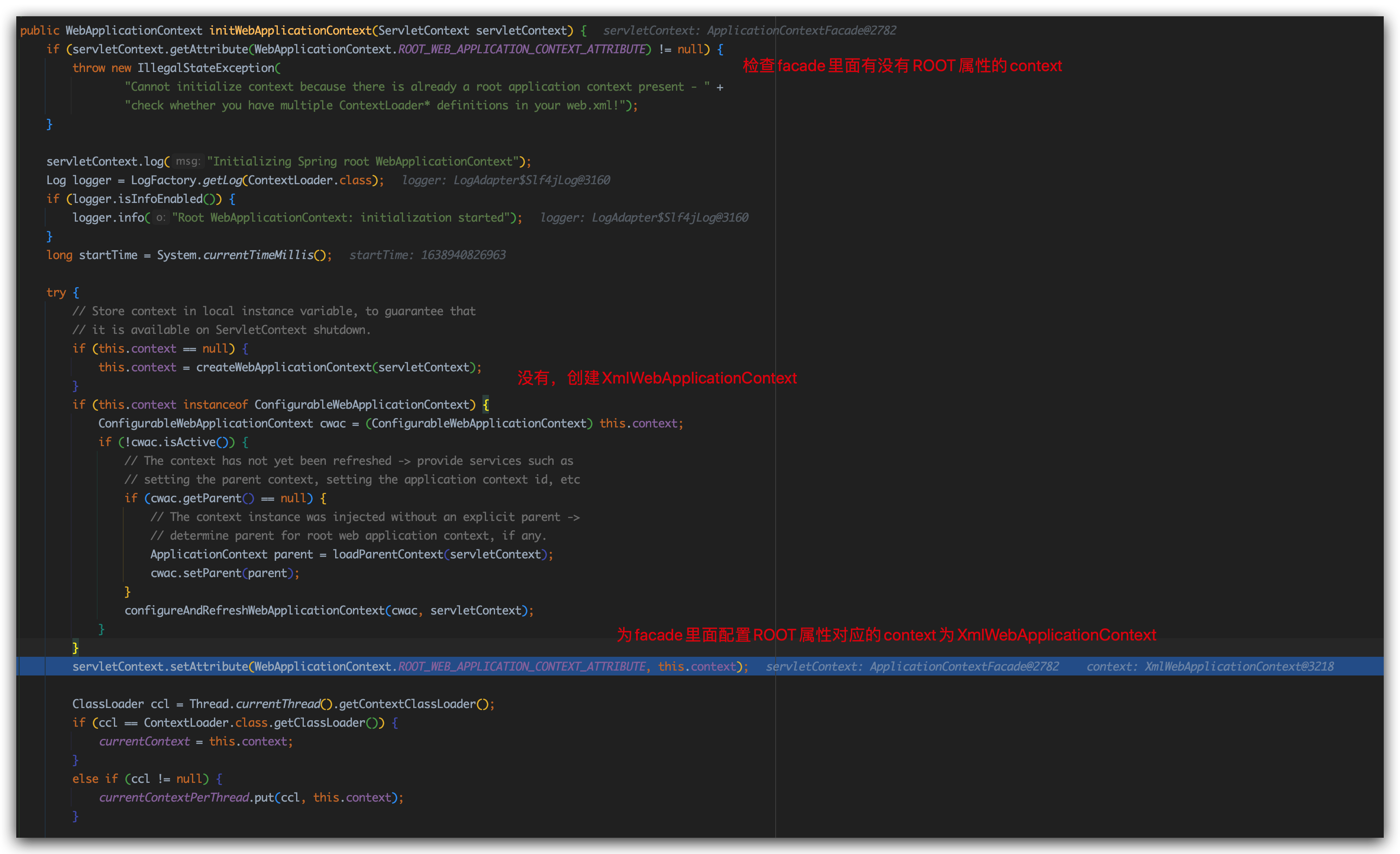
是的你没有看错,二者凭借成员属性“融合”到一起了。
Spring的Web应用上下文和Web容器的上下文应用就可以实现互访,二者实现了“融合”。我中有你,你中有我!
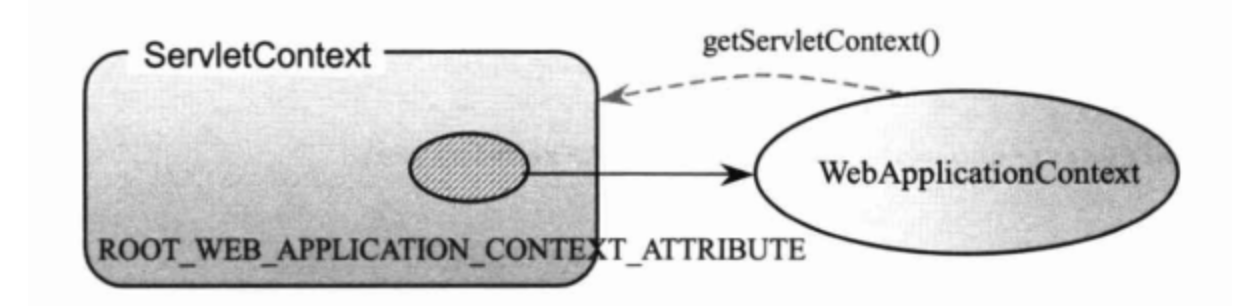
总而言之,Servlet规范中ServletContext实现(ApplicationContext)是tomcat的Context实现(StandardContext)的一个成员变量,而Spring的ApplicationContext是Servlet规范中ServletContext的一个属性。
DispatcherServlet
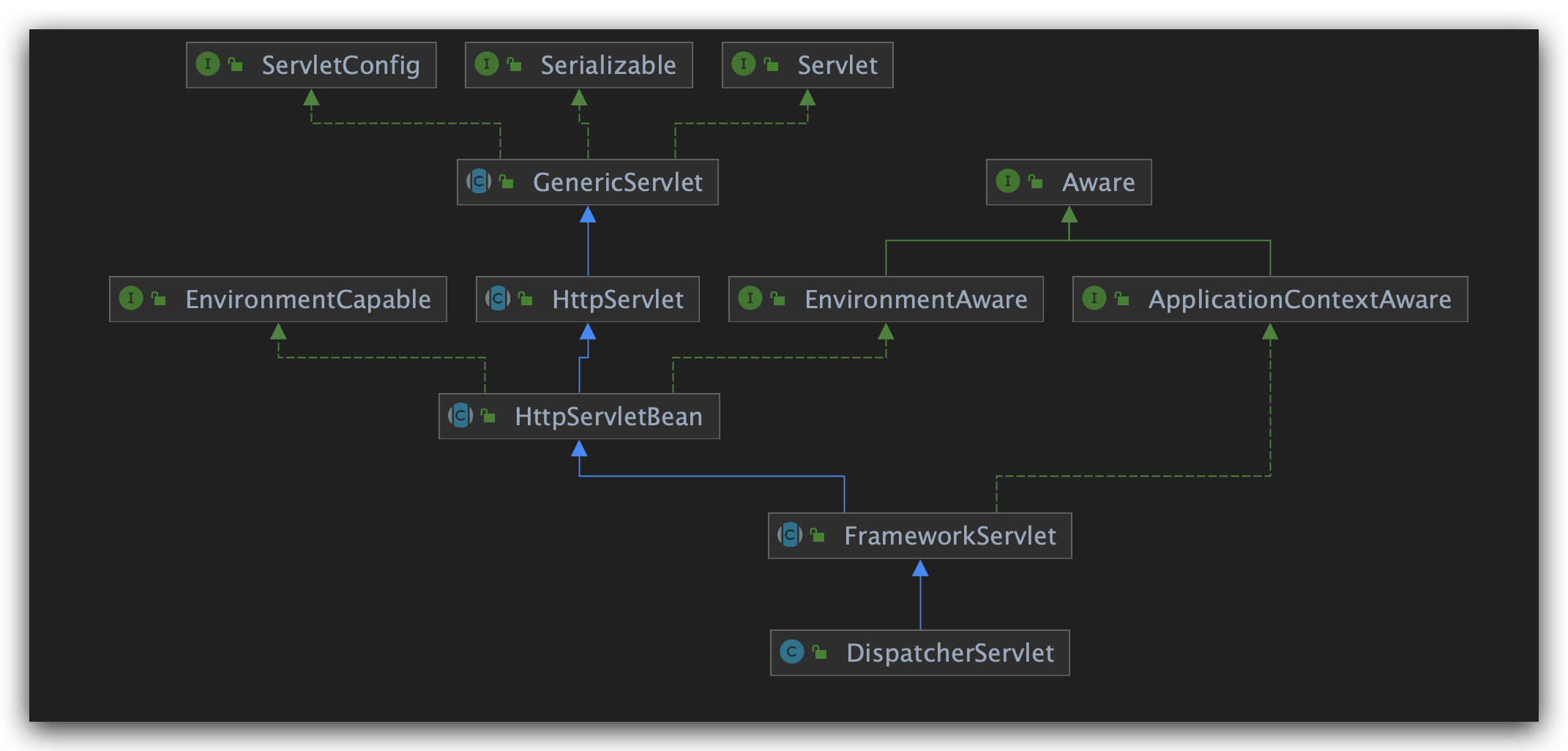
DispatcherServlet的本质是Servlet,是前端控制器。
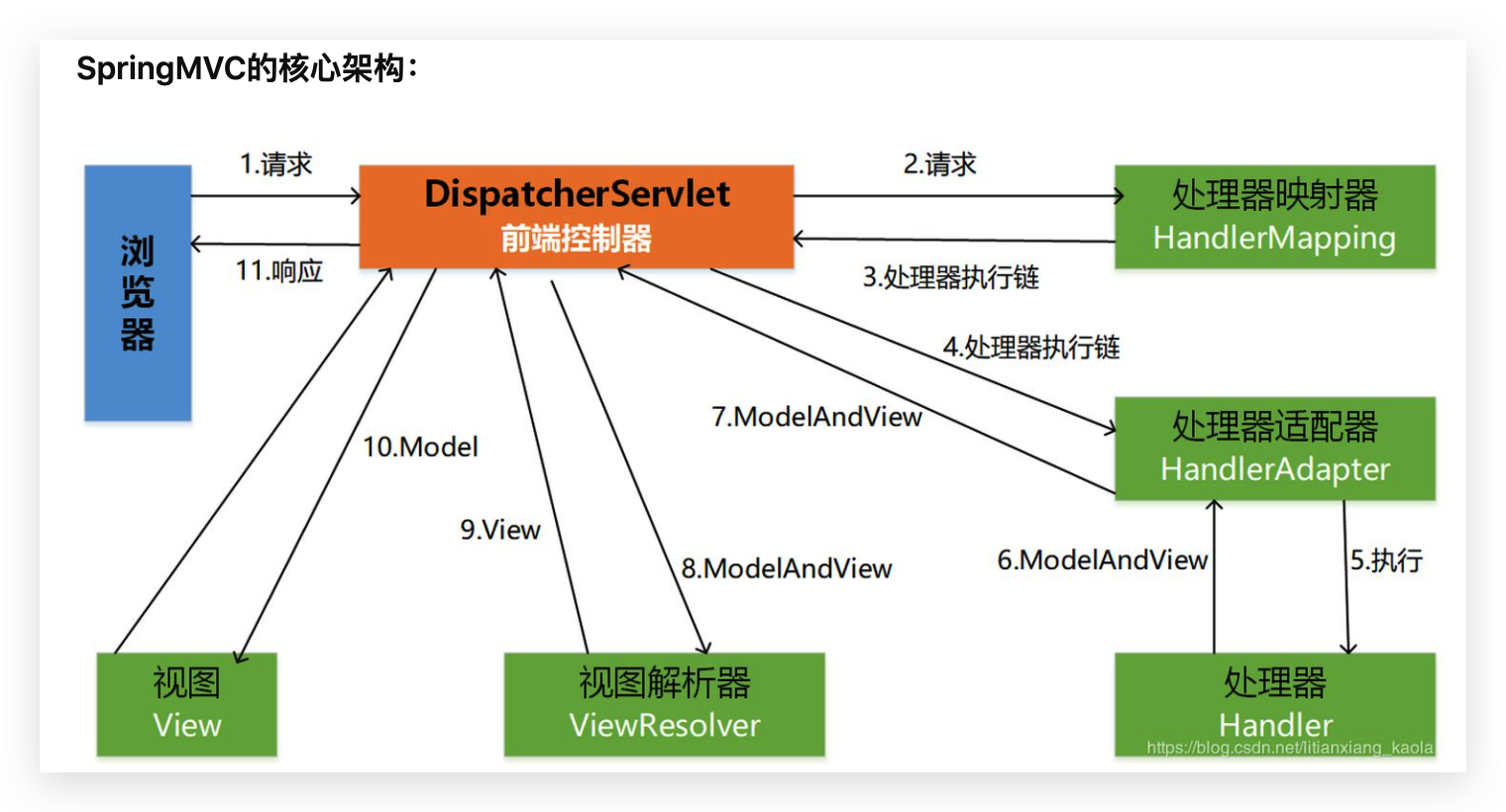
但是既然本质是Servlet,初始化还是要走init方法的。
还记得tomcat中的StandardContext.startInternal方法:
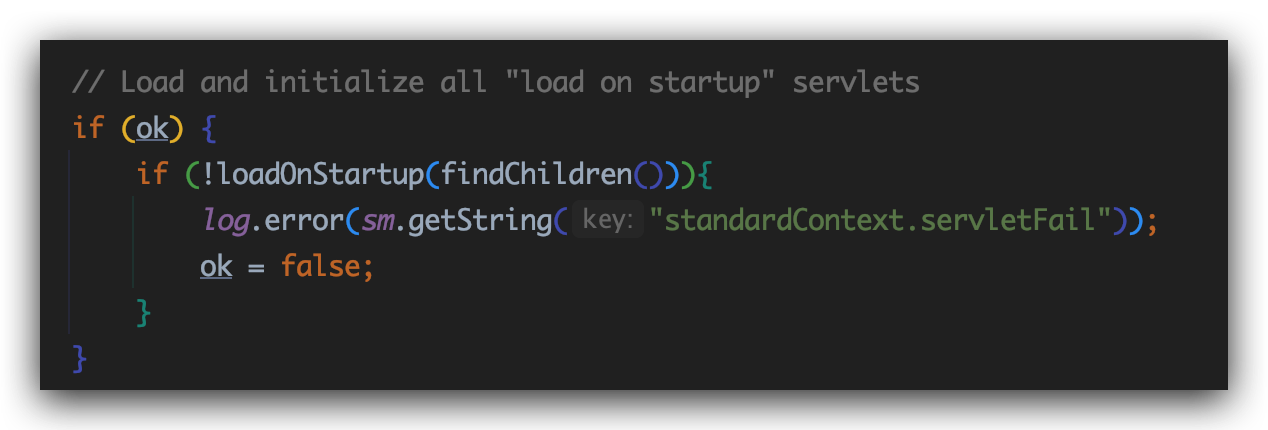
进入loadOnStartup方法:
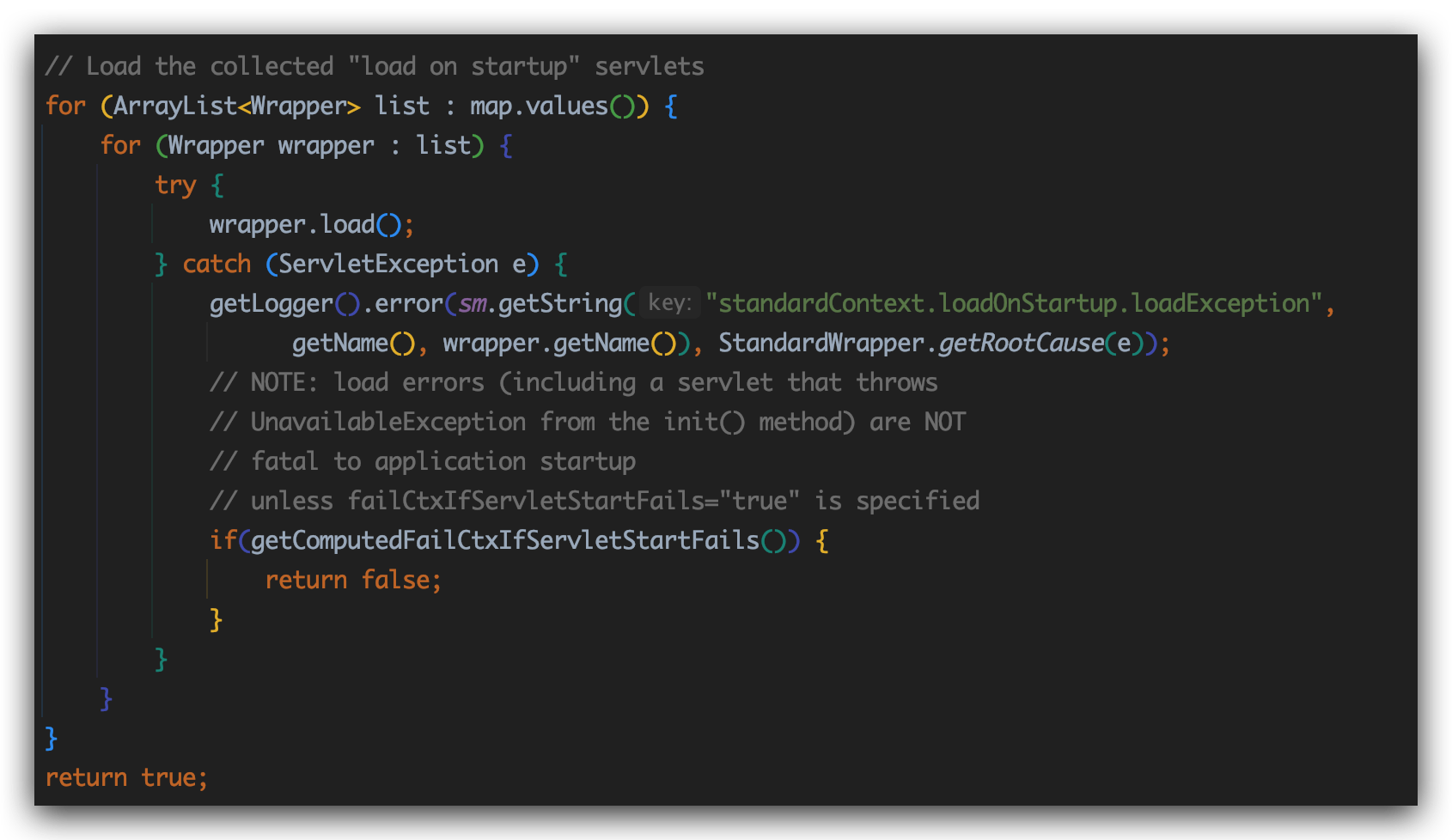
注释已经写的很清楚了,加载那些loadonstartup=1的Servlet
现在tomcat准备加载DispatcherServlet对象,要去寻找init方法
1 | GenericServlet (javax.servlet) |
在HttpServletBean找到了init方法
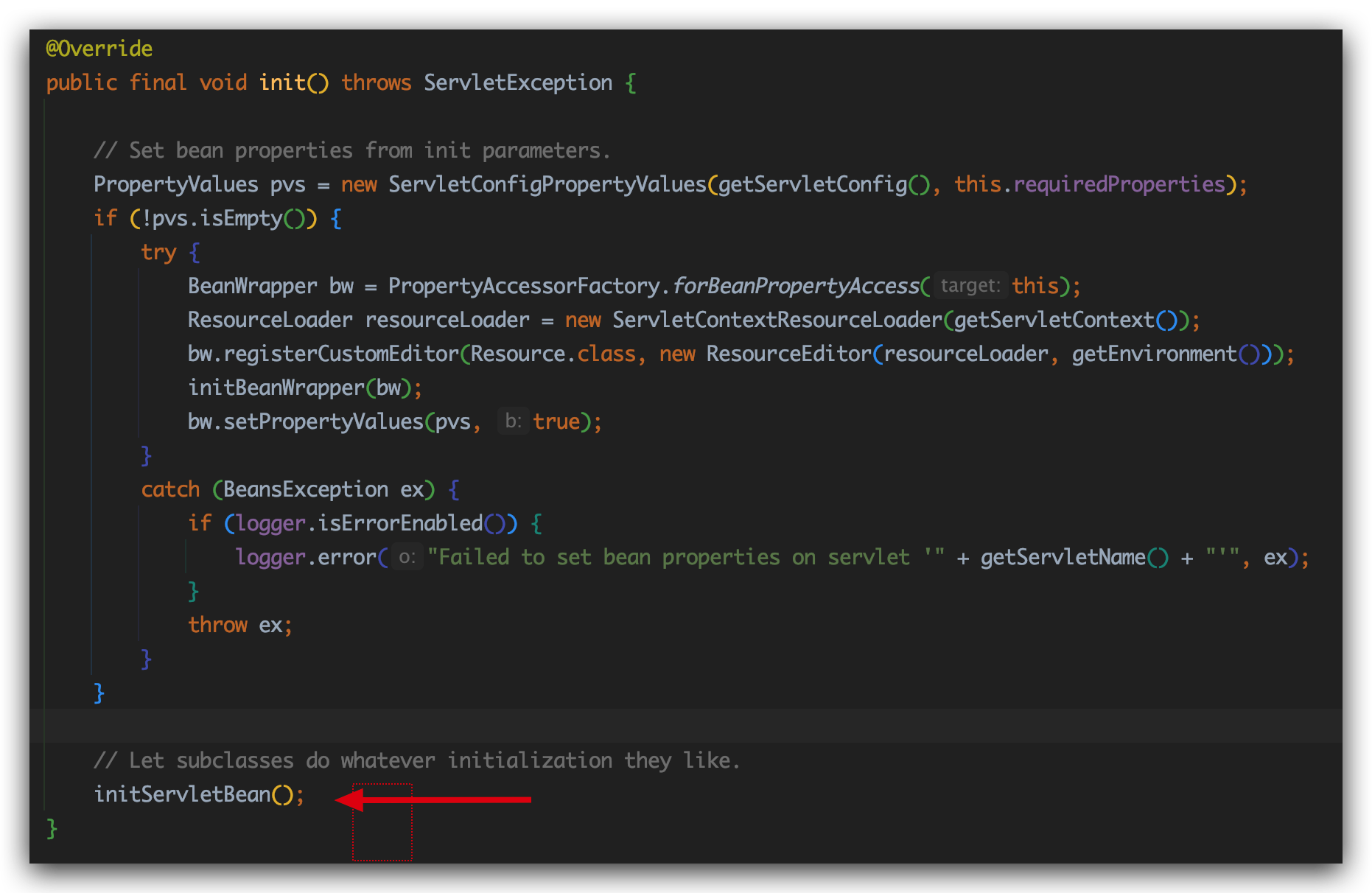
发现调用的是FrameworkServlet类的initServletBean方法:
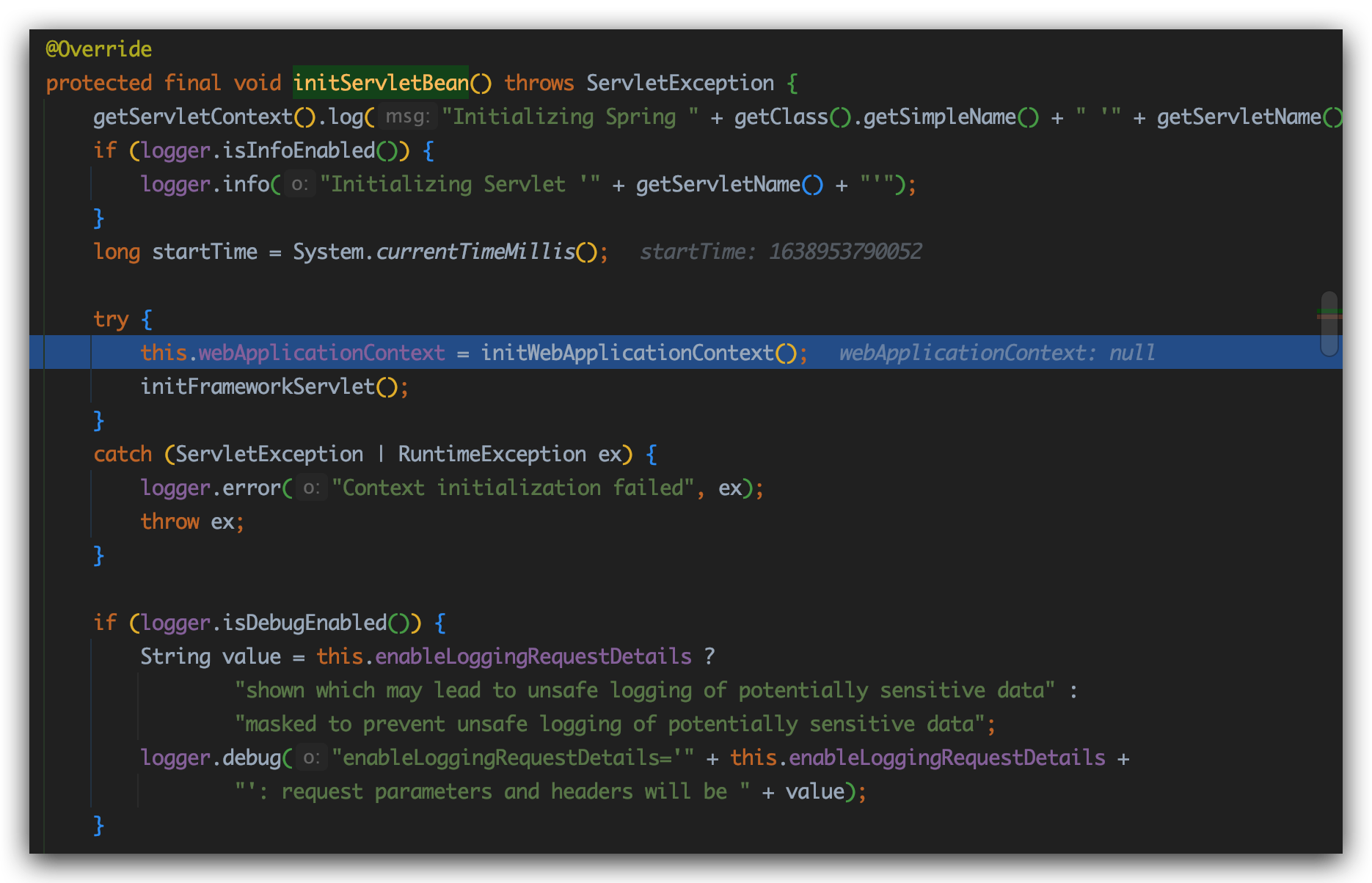
进入initWebApplicationContext方法:
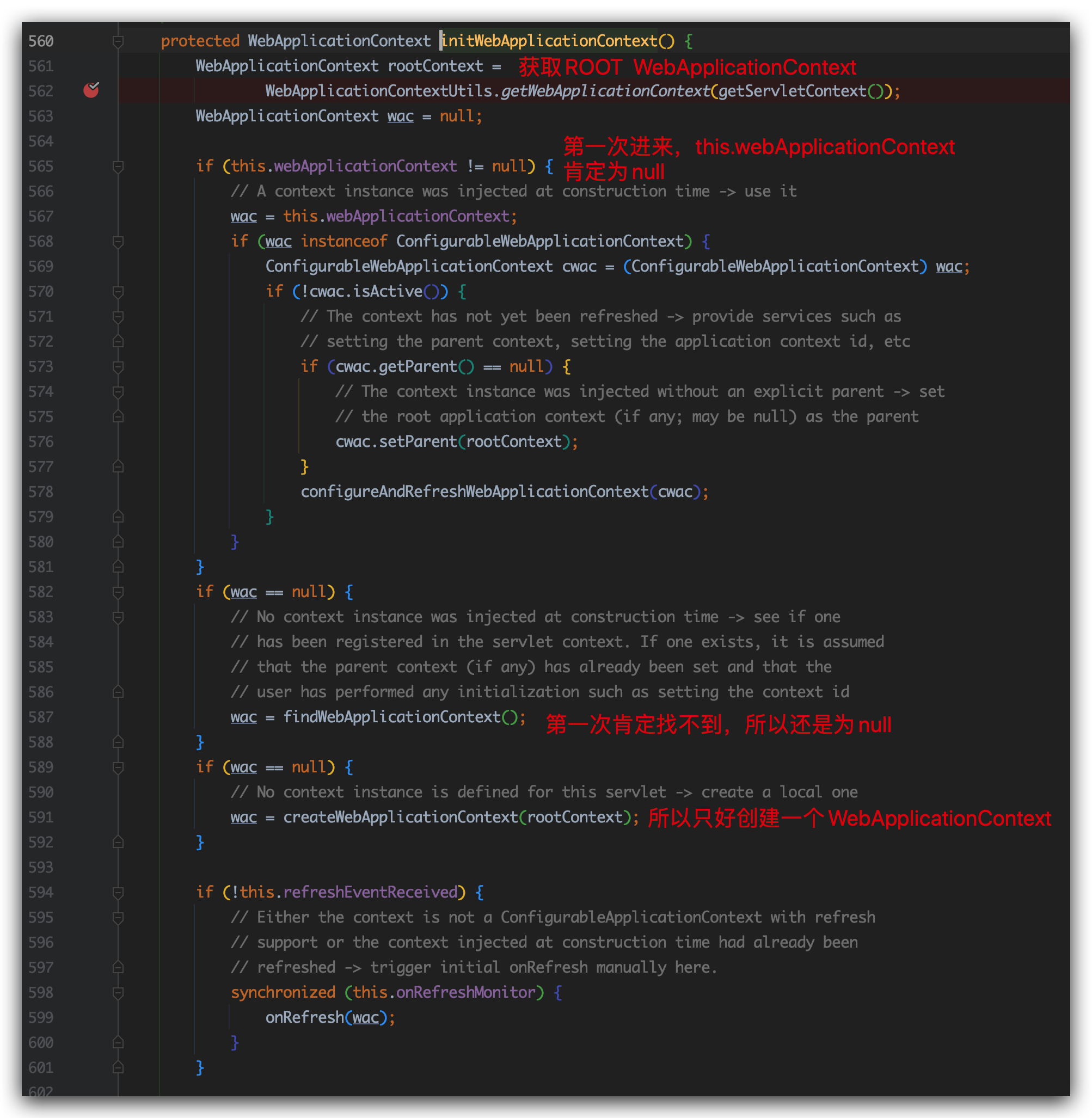
这里创建的是特定Servlet拥有的子IoC容器
根IoC容器做为全局共享的IoC容器放入Web应用需要共享的Bean,而子IoC容器根据需求的不同,放入不同的Bean,这样能够做到隔离,保证系统的安全性。
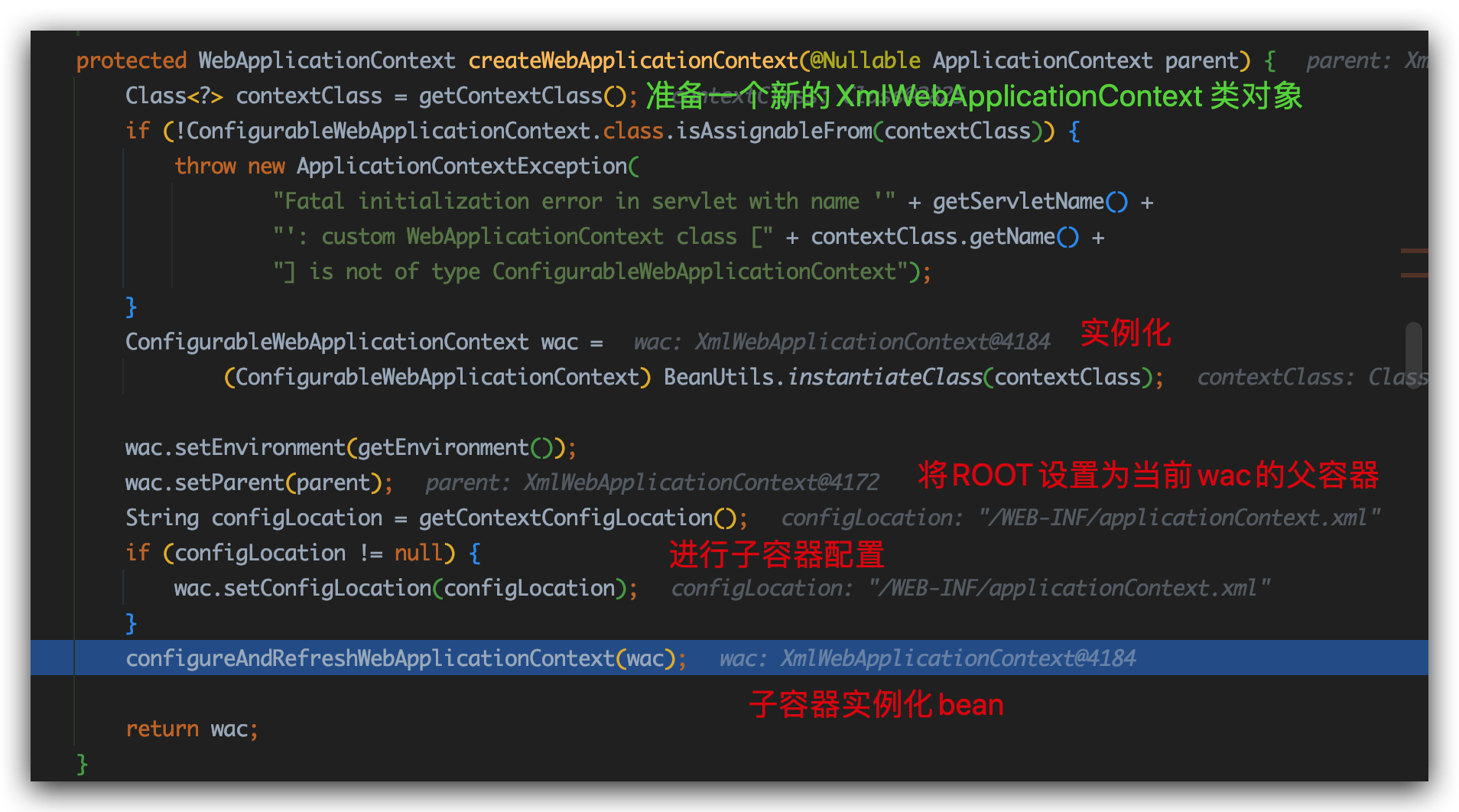
返回子容器
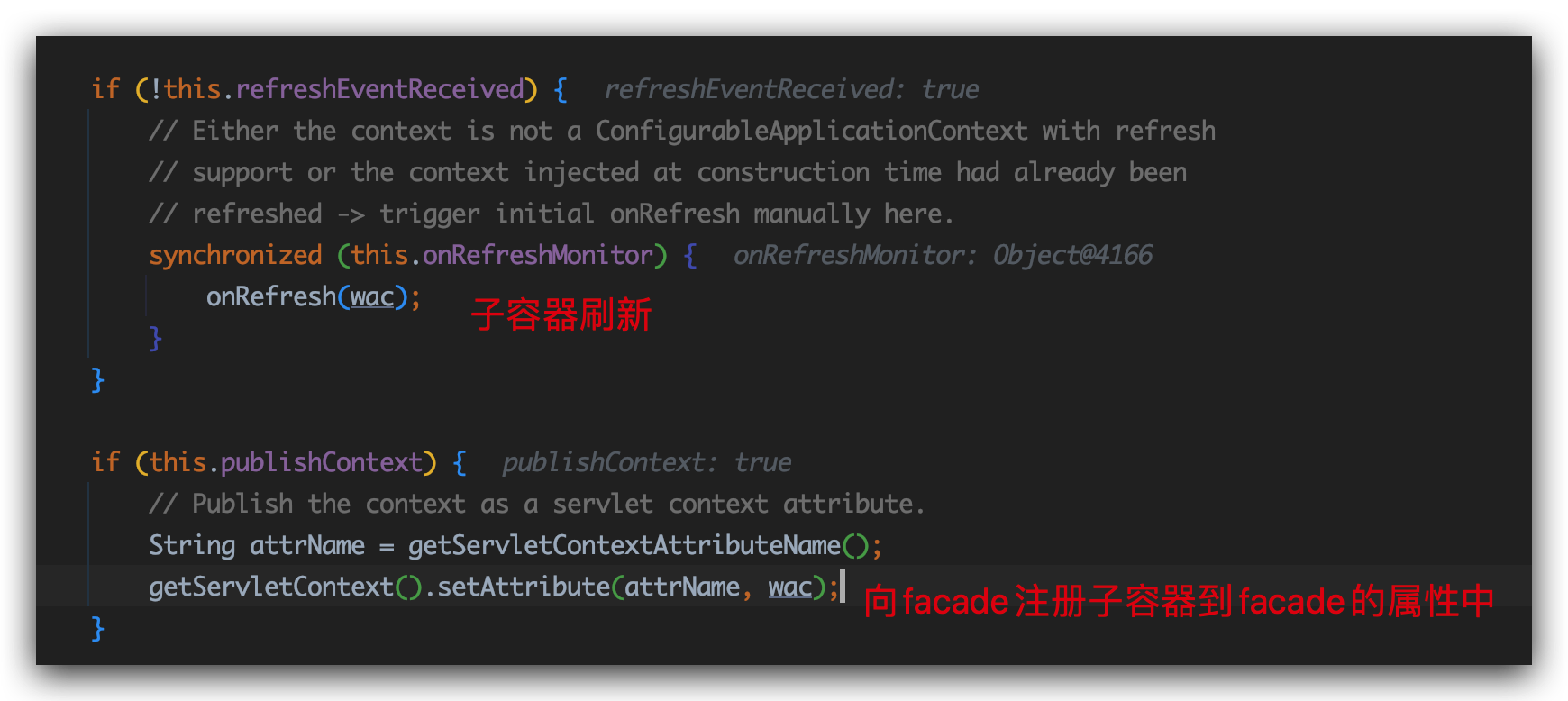
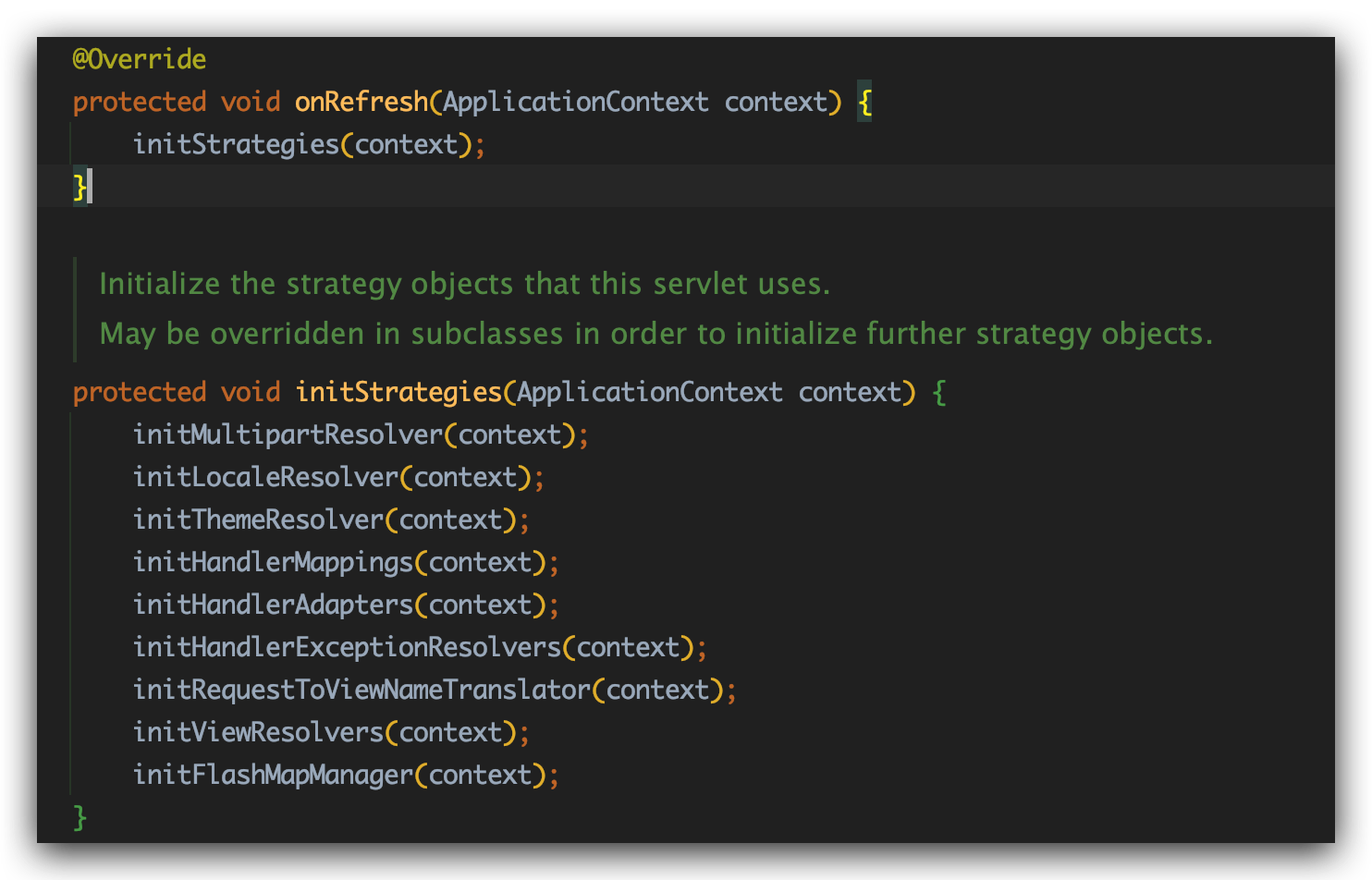
当IoC子容器构造完成后调用了onRefresh()方法,具体实现由子类覆盖,调用onRefresh()方法时将前文创建的IoC子容器作为参数传入,DispatcherServletBean类的onRefresh()初始化配置一堆组件
SpringMVC 启动流程
- tomcat会读取项目web.xml中的
<context-param>内容、<listener>标签、filter标签。 - tomcat会读取项目的web.xml中的
<listener>,如果配置了listener为ContextLoaderListener,那么就创建父容器ROOT,与tomcat的ApplicationContextFacade“融合”。 - 读取
servlet标签,一般是DispatchServlet - 为DispatchServlet创建子容器
- 读取
<servlet>标签的<init-param>配置的xml文件并加载相关Bean - onfresh方法创建SpringMVC的组件
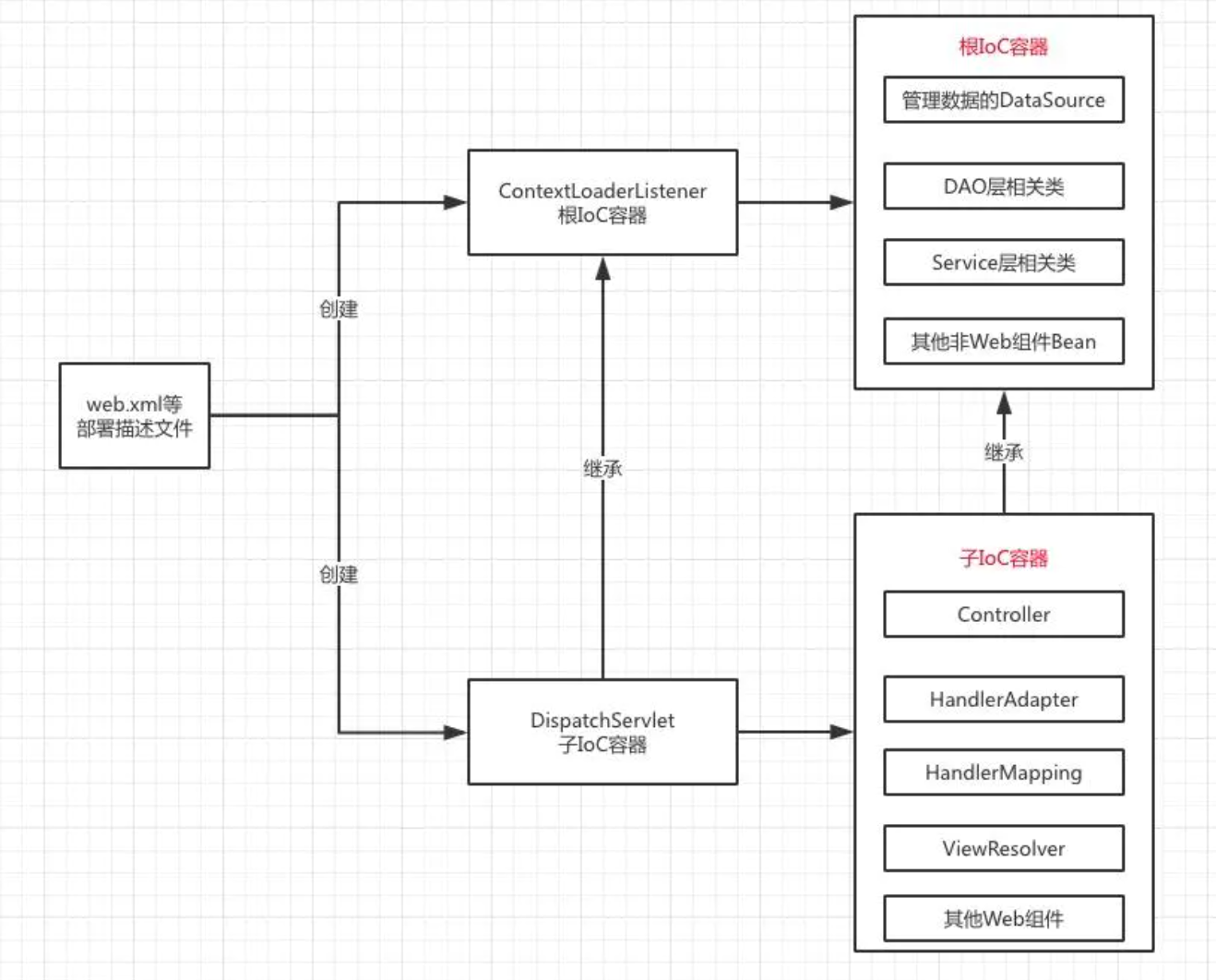
每个具体的 DispatcherServlet 创建的是一个 Child Context,代表一个独立的 IoC 容器;
ContextLoaderListener 所创建的是一个 Root Context,代表全局唯一的一个公共 IoC 容器。
四种方式获取当前容器
现在这句话应该可以清晰了:
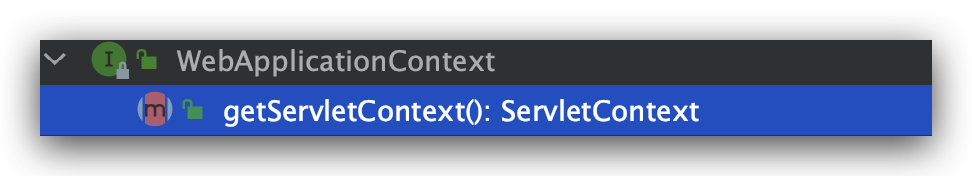
WebApplicationContext是专门为web应用准备的,从WebApplicationContext中可以获得ServletContext的引用。
同时,整个Web应用上下文对象将作为域对象属性放置在Web容器的facade中,以便Web应用可以访问spring上下文。
1 | // ROOT XmlWebApplicationContext |